Next: 5 Modularity Up: 4 Program specifications Previous: 4.1 Informal
In the Unified Modeling Language (UML), an activity diagram can be used to graphically illustrate the logic of a program. Similarly, pseudocode is also commonly used to describe the logic of a program. For instance, our log in logic may be expressed as follows:
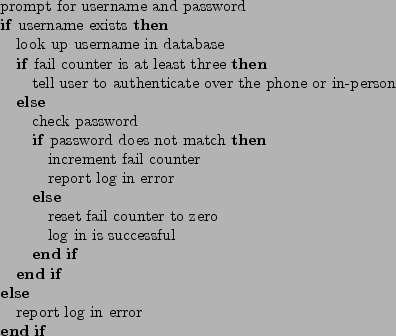
In an activity diagram or a piece of pseudocode, the logic of how to do something is already specified. Sometimes, this may not be the case. The specifications of a program can merely indicates the end result of the program, without any indication of how it is done.
For example, consider a program for sorting. It may be specified as follows:
inp[] with n elements
out[] with n elements
v found in inp[],
x in inp[]
x in out[]
out[], out[i] <= out[i+1] for all i
in the range of 0 to n-1
This doesn't tell us how to write a sorting program, it just specifies the outcome.
Copyright © 2006-08-21 by Tak Auyeung